- 1. What Is Goal Setting in Business?
- 2. Goal Setting Theory and Frameworks
- 3. How to Track and Measure Goals
- 4. SMART Goals: An Ultimate Guide With Examples
- 5. OKRs: The Ultimate Guide to Objectives and Key Results
- 6. What Is a Key Performance Indicator (KPI)?
- 7. What Is Management by Objectives (MBO)?
- 8. Goal Setting Templates
- 9. How to Achieve Goals and Ensure Success
- 10. Organizational Objectives: How to Set Them
- 11. Department Objectives: How to Set Them
- 12. How to Choose the Right Goal Setting Software
- 13. FAQ
- 1. What Is Goal Setting in Business?
- 2. Goal Setting Theory and Frameworks
- 3. How to Track and Measure Goals
- 4. SMART Goals: An Ultimate Guide With Examples
- 5. OKRs: The Ultimate Guide to Objectives and Key Results
- 6. What Is a Key Performance Indicator (KPI)?
- 7. What Is Management by Objectives (MBO)?
- 8. Goal Setting Templates
- 9. How to Achieve Goals and Ensure Success
- 10. Organizational Objectives: How to Set Them
- 11. Department Objectives: How to Set Them
- 12. How to Choose the Right Goal Setting Software
- 13. FAQ
What Is a Key Performance Indicator (KPI)?
This article was created with the assistance of an AI engine. It has been reviewed and revised by our team of experts to ensure accuracy and quality.
KPIs: The Ultimate Guide to Key Performance Indicators
“Have you set your KPIs for the quarter?” If this question strikes fear into your heart, keep reading.
Key performance indicators (KPIs) are a way for organizations to track their progress and measure their success. KPIs provide data-driven insights that allow businesses to make smart decisions, allocate resources appropriately, and maintain a competitive edge in the market.
This article explores and discusses:
- What KPIs are
- Their importance in business
- How to choose the right KPIs
- Examples of KPIs across various industries
- KPI dashboards
- Common challenges
- Tips for successful implementation and management
Before we dive into it, you can also unlock a free trial with Wrike to kick-start your goal setting processes. Wrike offers pre-built templates and collaborative features to set and track your KPIs with ease.
What is a KPI?
KPIs are measurable values that reveal whether a company is achieving its key business objectives. Think of a KPI as a compass that guides the company toward its strategic goals. A KPI can highlight performance, identify areas for improvement, and keep a business focused on what matters most.
The importance of KPIs in business
KPIs play a crucial role in modern businesses for several reasons:
- Performance measurement: KPIs provide objective data that let a company assess and manage how it’s performing in specific areas
- Performance improvement: KPIs guide employees to better performance, motivating them with clear targets and a sense of achievement
- Goal setting: KPIs help businesses set realistic, common targets for teams and individuals to work toward
- Decision making: By monitoring KPIs, businesses can make sound decisions, allocate resources effectively, identify trends, and anticipate challenges
- Accountability: KPIs create a sense of responsibility among employees by showing how their actions contribute to the success of the organization
- Communication: KPIs facilitate communication within the organization, ensuring that everyone is on the same page
How to choose the right KPIs for your business
Like Goldilocks, you’re looking for the KPIs that are just right. By selecting the right KPIs, you can accurately track your progress toward success. Here are some tips on choosing the most relevant KPIs for your business:
- Align KPIs with your strategic objectives: Link your KPIs directly to your business goals and vision
- Keep things simple: Focus on a limited number of KPIs that provide the most significant insights
- Make them measurable: Choose KPIs that can be quantified and tracked over time


- Ensure relevance: Your KPIs should be relevant to your industry, business model, and target audience
- Regularly review and update: As your business evolves, you’ll want to review and update your KPIs
KPI metrics: Categories and types
KPIs can be categorized by the aspect of business they measure. Here are some common categories and examples of KPIs:
Financial KPIs
- Gross profit margin: The percentage of profit generated from sales after accounting for the cost of goods sold
- Net profit margin: The percentage of profit remaining after accounting for all expenses
- Return on investment (ROI): The ratio of profits generated from investments relative to their cost
Operational KPIs
- Production efficiency: The ratio of output produced to the resources used in production
- Inventory turnover: The number of times inventory is sold and replaced within a specific period
- Order fulfillment time: The average time taken to complete and ship an order to a customer
Customer KPIs
- Customer satisfaction (CSAT) score: A measure of how satisfied customers are with a product or service
- Net promoter score (NPS): A metric that gauges customer loyalty by asking how likely they are to recommend a product or service to others
- Customer churn rate: The number of customers who cease doing business with a company during a certain period
People (human resources) KPIs
- Employee engagement: The level of commitment and enthusiasm employees have toward their work and organization
- Turnover rate: The percentage of employees who leave the company during a specific period
- Training effectiveness: The degree to which training programs improve employee skills and performance
Innovation and learning KPIs
- New product development time: The average time needed to bring a new product or service to market
- Patents: The number of patent applications filed by an organization
- Employee skill development: The improvement in employee skills and capabilities over time
KPI cascading: Aligning KPIs across the organization
Kind of sounds like a waterfall, right? You’re not far off. KPI cascading is the process of aligning KPIs from top-level strategic objectives down to employee goals. Cascading ensures that everyone in the organization is coordinating their efforts.
Here’s how to cascade your KPIs:
- Set clear strategic objectives at the top level
- Break down strategic objectives into departmental and team goals
- Assign individual goals that support team and departmental objectives
- Regularly review progress toward goals and adjust as needed
Setting and tracking KPIs
It’s important to set SMART targets to make KPIs specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound. Also, be sure to conduct regular performance reviews to track progress toward KPI targets and identify areas for improvement. These reviews should:
- Involve relevant stakeholders
- Be based on accurate, current data
- Include an action plan to address any performance gaps
- Be conducted at regular intervals to ensure ongoing progress monitoring
To effectively use KPIs, your business needs to set and monitor targets. Here’s how to do it:
- Be realistic: Base your KPI targets on historical data, industry benchmarks, and your organization’s capabilities — and make the targets realistic
- Communicate targets: Clearly communicate KPI targets to relevant teams and individuals, ensuring everyone understands their role in achieving them
- Monitor progress: Regularly track and analyze KPI data, identifying trends and making adjustments to stay on track
- Report and review: Share KPI progress reports with high-level stakeholders, discussing successes, challenges, and areas for improvement
Set your KPIs with ease
KPI examples
Here’s a list of strong KPI examples for different areas of work:
KPI examples for sales
- Sales revenue: The total amount of money generated from sales
- Average deal size: The average amount of money from each sale
- Sales pipeline: The number of potential sales opportunities at different stages of the sales process
KPI examples for marketing
- Cost per lead: The average cost of generating a qualified lead through marketing activities
- Conversion rate: The percentage of leads that convert into customers
- Social media engagement: The level of interaction with a company’s social media content (including likes, comments, and shares)
KPI examples for finance
- Operating cash flow: The cash generated from a company’s core business operations
- Debt-to-equity ratio: A financial ratio showing a company’s debt relative to its equity
- Budget variance: The difference between the planned budget and actual spending
KPI examples for customer service
- First response time: The average amount of time taken to respond to a customer inquiry
- Resolution time: The average amount of time taken to resolve a customer issue
- Ticket backlog: The number of unresolved customer support tickets
KPI examples for human resources
- Time to fill: The average amount of time it takes to fill a job opening
- Retention rate: The percentage of employees who remain with the company over a specific period
- Cost per hire: The total cost of hiring a new employee, including recruitment, training, and onboarding expenses
KPI examples for operations
- Capacity utilization: The percentage of an organization’s production capacity being used
- Overall equipment effectiveness (OEE): How well a company’s production equipment is being used
- On-time delivery rate: The percentage of orders delivered within the promised timeframe
KPI examples for software engineering
- Code quality: The level to which software code meets established standards for readability, maintainability, and efficiency
- Defect density: The number of defects per unit of code, indicating software quality
- Deployment frequency: The number of times new software releases are deployed within a specific period
KPI examples for project management
- Schedule performance index (SPI): How well a project is progressing compared to its planned schedule
- Cost performance index (CPI): How well a project is sticking to its budget
- Scope creep: The number of changes made to a project’s scope after the project has begun
KPI examples for PMO
- Project success rate: The percentage of projects completed on time, within budget, and achieving all objectives
- Resource utilization: The percentage of available resources (e.g., team members, equipment) being used effectively on projects
- Stakeholder satisfaction: The level of satisfaction among project stakeholders, including clients, team members, and executives
KPI examples for professional services
- Billable utilization: The percentage of a professional’s working hours that are billable to clients
- Client retention rate: The percentage of clients who continue to use a firm’s services over a specific period
- Average project margin: The average profit generated from a professional services project, expressed as a percentage of project revenue
KPI dashboard: Tracking and visualizing KPIs
It’s not just a matter of scribbling your KPIs down in a notepad — you need a proper way to visualize them.
A KPI dashboard is a visual tool that helps organizations track and analyze their key performance indicators. Dashboards provide real-time insights into performance so organizations can make data-driven decisions and adjust strategies as needed. Here are some benefits and key components of a KPI dashboard:
Benefits of KPI dashboards
KPI dashboards offer several benefits:
- Real-time data: Access up-to-date information on performance to make timely decisions
- Customization: Tailor the dashboard to display the most relevant KPIs for each user or department
- Data visualization: Highlight complex data in an easily digestible format through charts, graphs, and other visual elements
- Collaboration: Share dashboards with team members to promote transparency
Key components of a KPI dashboard
A KPI dashboard should include the following characteristics:
- Relevant KPIs: Choose KPIs that relate to the organization’s strategic objectives
- Simplicity: Keep the dashboard clean and uncluttered, focusing on the most important information
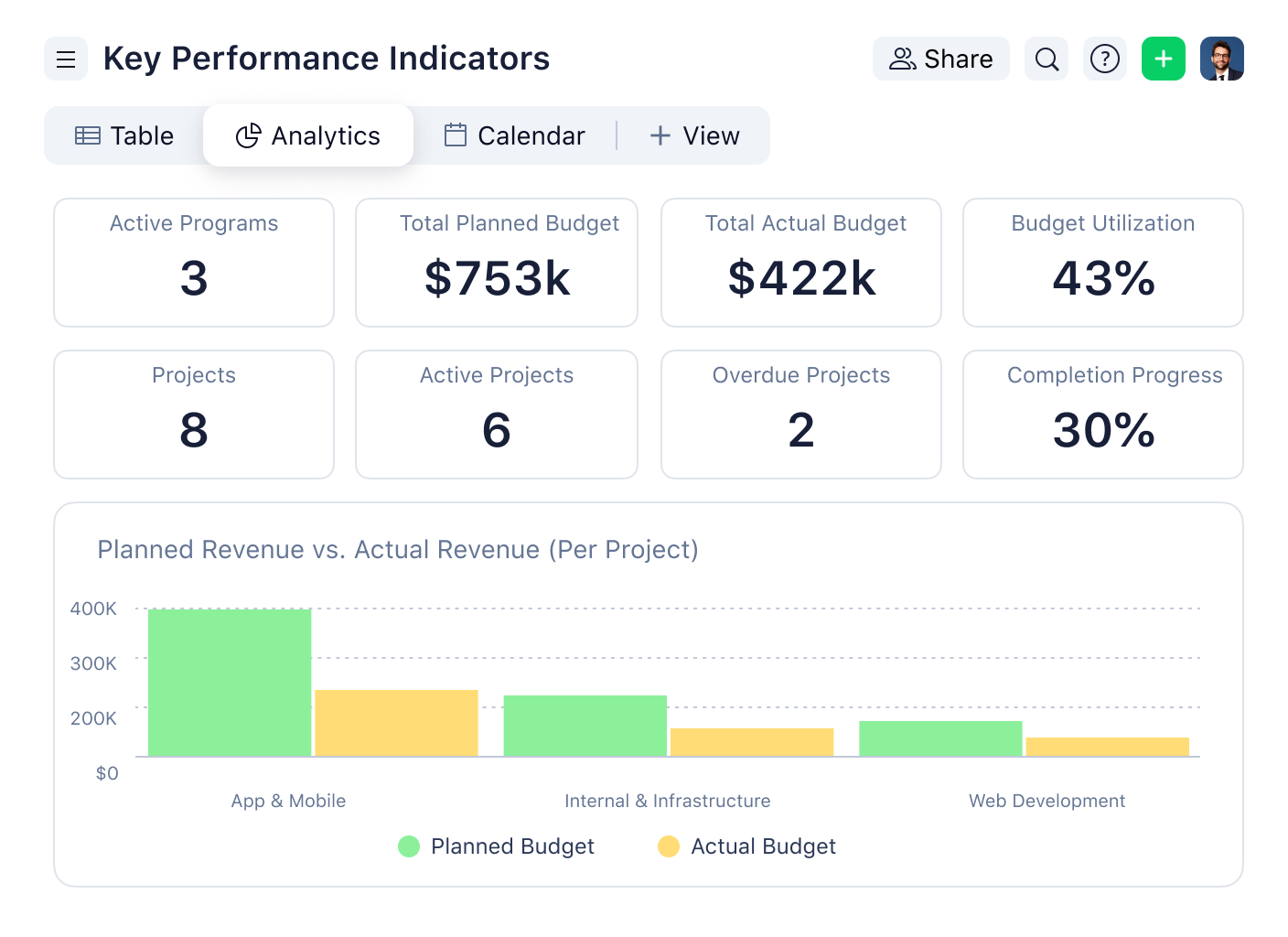

- Interactivity: Enable users to interact with the dashboard, filtering and drilling down into the data as needed
- Mobile compatibility: Make the dashboard accessible on all devices for use on the go
KPI dashboard tools and software
Various software tools are available to help businesses create and manage KPI reports. These platforms offer features such as data integration, customizable visualizations, and real-time updates. Some popular KPI dashboard tools include:
- Tableau
- Microsoft Power BI
- Domo
- Sisense
- Klipfolio
Wrike’s Tableau integration allows users to connect their Wrike data with Tableau to create powerful visualizations and in-depth analysis. Additionally, Wrike has its own robust dashboards and reporting features that provide users with real-time insights into their projects and team performance.
When selecting a dashboard tool, consider factors such as ease of use, integration capabilities, and scalability to ensure it meets your organization’s needs.
Common challenges and pitfalls in KPI management
Initially, you may face challenges as you try to manage your KPIs. We’ve outlined some common challenges below.
- Choosing the wrong KPIs: Focusing on irrelevant or poorly defined KPIs can lead to wasted resources and efforts
- Focusing on too many KPIs: Organizations should prioritize those KPIs that directly impact their strategic objectives in the long term
- Inaccurate or outdated data: Bad data can lead to incorrect analysis and poor decision making
- Lack of accountability: Improvements can be difficult to make if KPIs have no clear ownership
- Relying solely on lagging indicators: Combining leading and lagging indicators provides a more comprehensive view of performance
- Failing to adapt KPIs as business conditions change: Regularly reviewing and updating KPIs keeps them relevant to the organization’s goals
- Not clearly communicating KPIs to employees: It’s virtually impossible to manage KPIs when employees don’t know which KPIs they’re responsible for or understand how they contribute to the organization’s success
Tips for successfully implementing and managing KPIs
To overcome the above challenges and implement KPIs, consider the following tips:
- Align KPIs with strategic objectives: Ensure that KPIs directly support your specific business goals and vision
- Prioritize and focus: Select a few KPIs that provide the most significant insights into your organization’s performance
- Involve employees: Let employees help choose and monitor KPIs to create a sense of ownership and commitment
- Establish clear accountability: Assign responsibility for KPIs to specific individuals or teams to ensure progress
- Regularly review and update KPIs: As your business evolves, review and update your KPIs to be sure they make sense in light of your objectives
Set and track your KPIs with Wrike
So, now you know your KPIs from your OKRs and your ABCs.
If you want to measure performance, set goals, and make informed decisions in your business, try using KPIs. By selecting relevant KPIs and monitoring progress, you can achieve your strategic objectives and evolve your business.
Wrike offers customizable and pre-built templates for goal setting, easy collaboration across teams, and powerful dashboards to visualize progress. By using Wrike, you can document all the KPIs for your organization in one place and track progress in real time. Why not try it for yourself?